Kanban Methodology
Thu Feb 24 202213 min read
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a workflow management method for defining, managing, and improving services that deliver knowledge work.
It aims to help you visualize your work, maximize efficiency, and improve continuously.
Definition
The Japanese word “kanban”, meaning “visual board” or a “sign”, has been used in the sense of a process definition since the 1960s.
The systems Toyota used to limit their work in progress have been called “kanban systems”.
On the other hand, the capitalized term “Kanban” is known and associated with the emergence of the “Kanban Method,” which was first defined in 2007.
Roots of Kanban
Kanban arose as a scheduling system for lean manufacturing, originating from the Toyota Production System (TPS). Toyota introduced “Just in Time” manufacturing in late 1940s.
Kanban represents a ”Pull System”. Production is based on customer demand rather than the standard push practice to produce goods and push them to the market. This laid the foundation of Lean manufacturing.
Core purpose is minimizing waste activities without sacrificing productivity. The main goal is to create more value for the customer without generating more costs.
Kanban Principles
Kanban principles can be broken down into 2 main categories.
- Change Management Principles
- Service Delivery Principles
Change Management
Practice 1: Start With What You Do Now
Kanban gives the flexibility to use existing workflows, systems and processes. It strongly believes - “Don’t disrupt what is in place”.
Kanban recognizes that existing processes, roles, responsibilities, and titles have value and are, generally, worth preserving. It will highlight issues that need to be addressed.
Kanban will help to assess and plan changes so their implementation is as non-disruptive as possible.
Practice 2: Agree to Pursue Incremental, Evolutionary Change
It is designed to meet minimal resistance. It also encourages continuous small incremental and evolutionary changes to the current process (collaboration and feedback).
Sweeping changes are discouraged strictly.
Practice 3: Encourage Acts of Leadership at All Levels
Kanban strongly encourages leadership at all levels, which derives from people’s everyday insights. As a result it acts to improve their way of working.
Each shared observation fosters a continuous improvement mindset (Kaizen) to reach optimal performance.
This can’t be a management-level activity i.e. it has to be adopted at the very ground level.
Service Delivery
Practice 1: Focus on Customer’s Needs and Expectations
Delivering value to the customer should be at the centre of each organization. They need to understand the needs and expectation of your customer.
Kanban brings attention to the quality of the provided services and value it creates.
Practice 2: Manage the Work (not the people)
- Empower people’s abilities to self-organize around the work.
- Focus on the desired outcomes.
- Avoid micromanaging the people delivering the services.
Practice 3: Regularly Review the Network of Services
- Requires continuous evaluation to foster a customer service culture.
- Regular reviews and outcome assessment encourages the improvement of the delivered results.
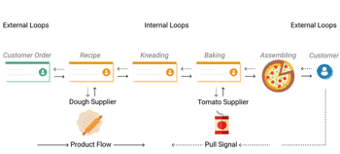
Pull Systems
A Pull System lets you consume, only when you have a demand, at the right time. (like, Buying a ticket to watch a movie).
It uses Lean technique for reducing the waste of any production process.
It allows you to start new work, only when there is customer demand for it. It also helps you to reduce overhead and optimize storage costs.
Why is pull better than push?
Some advantages of Pull System over Push System are -
- Work is pulled only if there is a demand for it.
- Build products based on actual demand and not on forecasts.
- Identify bottlenecks in the process
- Prioritize tasks better
- Avoid overloading the team
- Deliver value not tasks
Advantages of Pull Systems
Advantages of Pull systems are -
- Quickly adapt to change, that may occur in the work process.
- Scale the optimal capacity of your team
- Deliver work items much faster
- Reduce waste of resources
- Increase productivity
- Improve flow efficiency
Applying Pull Systems - Kanban Boards
The best way to apply pull signals so is by building a visual workflow where all valuable information can be recorded and tracked.
This will help to acquire a full overview of your work process and catch all important signals
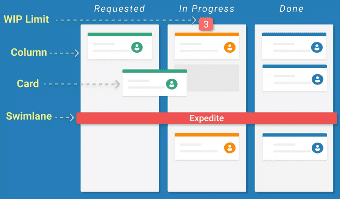
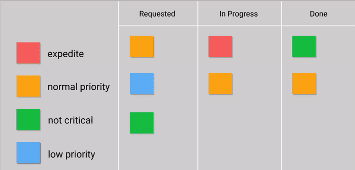
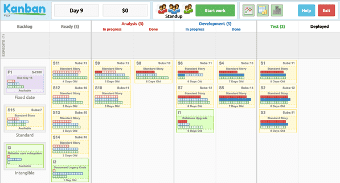
Kanban Board Elements
Kanban Cards
This is the visual representation of tasks. Each card contains information about the task and its status, such as deadline, assignee, description, etc.
Kanban Columns
Each column on the board represents a different stage of your workflow. The cards go through the workflow until their full completion.
Work-in-Progress Limits
They restrict the maximum amount of tasks in the different stages of the workflow. Limiting WIP allows you to finish work items faster by helping your team focus only on current tasks.
Kanban Swimlanes
These are horizontal lanes you can use to separate different activities, teams, classes of service, and more.
Using Kanban Boards Efficiently
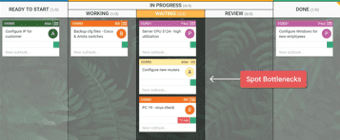
Spot Workflow Bottlenecks
If tasks arrive faster than they leave, work will start to pile up. This may be caused by a temporary issue or a bottleneck in your process.
Using Kanban Board you can act swiftly to resolve it and prevent it from occurring again.
Limit Work in Progress and Focus
Great way to discourage your team from multitasking by applying WIP Limits.
It is very important to focus on finishing work instead of starting a new one.
We create value by delivery.
Kanban Dashboard to Save Time Wasted on Unnecessary Meetings
Using Kanban Dashboard, you can save much time spent on meetings, progress reports, and many other unnecessary interruptions. Board will serve as a dedicated information repository.
It will spread knowledge about who is doing what at any time. And also, will keep everyone in the team in the loop about how assignments are progressing.
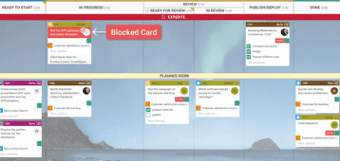
Visualize Work Blockers
You will be able to visualize problems that prevent your team from completing any given task.
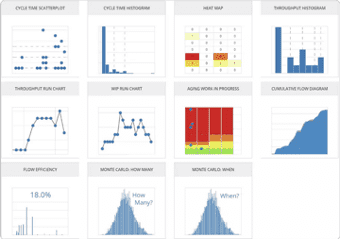
Collect Key Workflow Metrics and Improve
Kanban Software products automatically gather information about your tasks’ cycle time, lead time, and other key performance indicators.
This will help you make data-driven decisions about any changes to your process and save you plenty of time otherwise wasted on collecting metrics by hand.
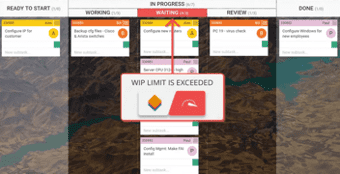
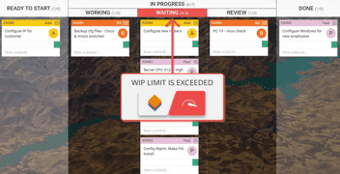
WIP Limit
The acronym WIP stands for Work In Progress. WIP is the number of task items that a team is currently working.
It frames the capacity of your team’s workflow at any moment. Limiting work in progress is one of the core properties of Kanban.
It allows you to manage your process in a way that creates a smooth workflow and prevents overloads.
By applying WIP limits, your team has the opportunity of locating bottlenecks in their working processes before they become blockers.
How to set up WIP Limits
There is no one way to set up WIP Limits. It depends on continuous improvement and differs from team to team. Some important points to keep in mind while defining WIP limits -
- Review how you deliver your services on a team level and consider how work items are aging on your board
- Remember that your workflow will be changing dynamically
- Monitor your team’s workflow regularly
- Control how you limit WIP depending on the ever-changing factors
- It is usually a good practice not to exceed WIP limits
Benefits of using WIP Limits
Some major benefits of WIP limits are -
Keep Optimal Work Pace
- Keep an optimal work pace without exceeding its work capacity.
- Kanban WIP limit is the gatekeeper that makes sure you start only as much work as you finish throughout the organization
- Prevents the accumulation of unfinished work
Reveal Process Blockers
- Will help reveal work process blockers and prevent team members from regular context switching between tasks
- Will have a positive impact on efficiency and will improve your team’s productivity
Prevent Multitasking
- Would prevent context-switching
- Reveal the difference in throughput rates
- Exceeded limits would signal the need to review the process
- Potentially look for ways to increase capacity in the heavier work stage
Deliver Value Faster
- Will help you complete the number of active work in progress faster
- The more active work you have in your system, the slower real customer value is delivered
- Limiting WIP improves your delivery rate (throughput), so you can continuously meet or exceed customer expectations
Why use WIP Limits?
WIP limits are the best way to build a pull system. It is a journey in which you have to travel to achieve excellence.
Setting the right WIP limits is part of the continuous improvement process. It changes over time when members join or leave the team along with other variable factors like efficiency.
Be mindful and honest about your limits when you have to change them.
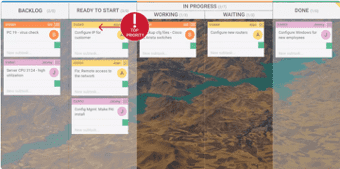
Prioritizing Tasks with Kanban
Prioritizing work tasks is always a challenge. Kanban helps you to arrange tasks based on their importance and resolve urgent issues as fast as possible.
Set some basic rules on your Kanban board and make sure your team is strictly following them.
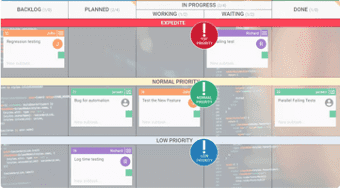
Prioritize Work with Kanban Columns
Board starts with a column called “backlog”. This is the place where you put all future work and ideas.
Next is the “requested” or “ready to start” column that serves as the entry point of work items to your workflow.
There can be different types of waiting Kanban columns further in the workflow on your board, depending on your team’s functionalities.
For each of them, your team needs to follow the rule of pulling top cards first—this way, the tasks of the highest importance will be completed as fast as possible.
Generally, by using Kanban, you create a pull system where team members pull their next task after finishing their current one.
When you place future tasks in a waiting Kanban column, you need to make sure that the top ones will be of the highest importance.
Prioritizing Tasks with Kanban Swimlanes
Swimlanes can also serve as a tool for prioritizing your Kanban board’s tasks.
Using Kanban swimlanes for task prioritization, you can be sure that valuable work items will be completed prior to others. The whole process’s visualization will help you notice weak spots in your workflow and continuously improve it.
The Kanban Backlog
Backlog is the space where you place work items or ideas that will be done in the near or distant future.
There is no guarantee that all tasks in the Kanban Backlog will be delivered. The items in this column are more like an option the team has for future work rather than a commitment point.
Prioritizing the Kanban backlog
Backlog is a place where your team plans all future work. It can easily become a messy place with tons of ideas.
Team needs to review all items in the backlog to ensure that it contains the appropriate items and prioritize them.
This should be an ongoing activity or, even better, an activity that occurs regularly.
Kanban in Practice
The whole process can be broken down in to these following steps.
Step 1 - Visualize the Workflow
- Start with a board with cards and columns
- When you start working on item X, you pull it from the “To Do” column, and when it is completed, you move it to “Done”.
- Easily track progress and spot bottlenecks
Step 2 - Limit Work in Progress (WIP)
- Ensure a manageable number of active items are in progress at any one time
- If there are no work-in-progress limits, you are not doing Kanban
- Switching a team’s focus halfway through will generally harm the process
- Multitasking is a sure route to generating waste and inefficiency
Step 3 - Manage Flow
- Managing the flow is about managing the work but not the people
- Flow means movement of work items through the production process at a predictable and sustainable pace
- One of the main goals when implementing a Kanban system is to create a smooth, healthy flow.
- Focus on managing the work processes and understanding how to get that work faster through the system
Step 4 - Make Process Policies Explicit
- Can’t improve something you don’t understand
- Process should be clearly defined, published, and socialized
- People would not associate and participate in something they do not believe would be useful
- When everyone is familiar with the common goal, they would be able to work and make decisions regarding a positive impact
Step 5 - Feedback Loops
- Implementing feedback loops is a mandatory step.
- They ensure that organizations are adequately responding to potential changes and enable knowledge transfer between stakeholders
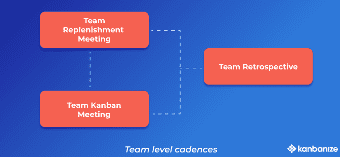
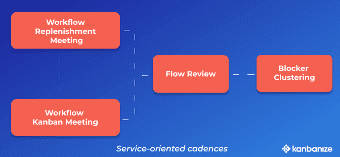
- An example of a team-level cadence is the daily Team Stand-ups for tracking the status and the flow of work
- Service-oriented cadences in Kanban, such as operations, service delivery, and risk meetings, aim to synchronize and improve your delivery of service
Step 6 - Improve Collaboratively
- Collaboratively implementing changes based on scientifically proven methods, feedback, and metrics.
- Cultivating an organizational culture where every hypothesis is proven to have positive or negative results is crucial for developing a mindset focused on improvement through evolutionary change
Key Takeaways
- Pursue Incremental, Evolutionary Change
- Focus on Customer’s Needs and Expectations
- Manage the Work (not people)
- Visualize your workflow
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP)
- Focus on completing features, than starting new ones
- Spot Bottlenecks early in the process and remediate them
- Continuously improve your workflow with feedback loops
- Always Pull Work never Push
Learn Kanban by playing
One of the best ways to learn and practice Kanban is the Kanban Board Game
It is a free single player game, but can be played within a team.
The goal is to maximize revenue by getting more features done. It enforces strict WIP limits which forces the player to understand the core principles of Kanban. It will help you to understand how to get the flow with a cross-functional team.
I hope you have learned something about Kanban today and will get better with continuous improvement.